what test for rotator cuff tear|complete rotator cuff tear test : trading Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as . WEB1080p 9:01. dando a bunda de quatro e tomando gozada usando legging e salto alto. 255 223 visualizações 82% 1080p 12:00. BANGBROS - Brazilian Gostosa Abby Lee Brazil .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Descomplica São Paulo faz agendamento gratuito de serviço.
Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as . Doctors can diagnose a torn rotator cuff by doing a physical examination, ultrasound, x-ray or MRI. These exams will help them .
When rotator cuff pathology is suspected, we can use some maneuvers to test the integrity of the four tendons that make up the cuff:- Infraspinatus- Supraspinatus- Subscapularis- Teres minor Rotator Cuff Tear. A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm. You may have shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries .Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as .
Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder.Definition/Description. There isn’t an exact definition of a massive rotator cuff tear. Sometimes the severity is expressed by the number of tendons which are torn, sometimes on the size of the tear. Lädermann et al. speak of a rotator .
Rotator cuff injuries are most often caused by progressive wear and tear of the tendon tissue over time. Repetitive overhead activity or prolonged bouts of heavy lifting can .
Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. Diagnosis can . Doctors use a variety of tests to diagnose rotator cuff problems. Imaging tests, such as an MRI, are especially important for figuring out the specific cause of your pain. Differential Diagnoses . . Small rotator cuff .
special tests for rotator cuff tear
sebbag schirmer tear test repeat
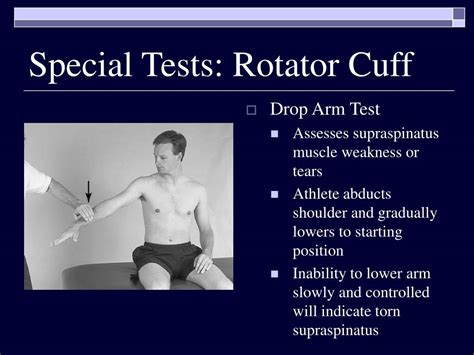
Rotator cuff injury runs the full spectrum from injury to tendinopathy to partial tears, and finally complete tears. Age plays a significant role. . When considering a rotator cuff tear, there are variations in the tests noted above. If the patient cannot hold the empty can test position, it is called a drop arm test. Next is the external .The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more .
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers the arm to . A rotator cuff tear is a rip in the muscles stabilizing your shoulder. Explore symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention tips to manage and recover effectively.To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. Evidence [ edit | edit source ] Based on the Park et al [1] study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator .
Occasionally, patients younger than 35 get partial tears of the rotator cuff. These tears may be associated with an injury. Partial rotator cuff tears are common in people who are overhead athletes (they play sports with an upper arm and shoulder arc over the head), such as pitchers in baseball. Partial rotator cuff tears in competitive . most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus. Infraspinatus Strength. technique. with the pateint's elbow in 90 degrees flexion, the arm at the side and internally rotated 45 degrees, external rotation strength can be checked against resistance by the examiner.
selected tear film tests in healthy cats
A rotator cuff tear is a tear in the group of four tendons and muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. Learn about symptoms and how it is treated surgically or conservatively. . Your healthcare provider may order one or several imaging tests to diagnose your condition accurately, including: X-rays; Ultrasound of the shoulder; MRI of the shoulder; This is the most common way to diagnose a rotator cuff tear and what type of tear it is. MRI results can provide information about the tear that can help the provider make certain decisions .An injury to the rotator cuff, such as a tear, may happen suddenly when falling on an outstretched hand or develop over time because of repetitive activities. . This test uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body. A rotator cuff may tear partly or .The following Cluster Tests were retrieved from Roy et al. (2015): Hawkins-Kennedy test; Neer's test; Painful arch sign; Empty can test . However, surgical treatment for chronic and large rotator cuff tears needs to be improved, especially for those in elderly patients, who continue to demonstrate high failure rates. For irreparable rotator .
Rotator cuff injury test types. Which tests are performed may depend, in part, on whether your suspected rotator cuff injury is in the supraspinatus, subscapularis, or infraspinatus. and to determine whether the tendons that lie between the humerus and the acromion are being pinched . Welcome to the club. Rotator cuff issues are common, an unfortunate side effect from the wear and tear of daily life. More than 2 million Americans visit their doctor every year because of rotator .
This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests .This type of shoulder test, or rotator cuff injury test, is used to identify tears within the muscle group of the rotator cuff. Shoulder Shrug Test; This torn rotator cuff test checks if the patient imitates a shrug movement when trying to actively raise their arm. The patient is unable to raise the arm to a 90 degree elevation without raising . Finally, the “painful arc sign” has high sensitivity (97.5 percent) as a single finding, making it helpful in ruling out rotator cuff tears when absent. 2 The test is performed by having the .
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is the most common cause of shoulder pain. The supraspinatus tendon is most frequently involved and the subscapularis is second. Active abduction in an arc of 40 to 120° and internal rotation cause pain (see symptoms and signs of rotator cuff injury).Passive abduction causes less pain, but abduction against resistance can increase pain. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles critical for the strength, stability and function of the shoulder. Tears of the rotator cuff tendons are a common source of shoulder pain, weakness and other problems. Imaging studies, such as radiographs, MRIs or ultrasounds, are used to evaluate rotator cuff tears. Physical therapy and the occasional use of cortisone . The Neer's test merely reveals if you have shoulder impingement; it doesn't reveal what structure in your shoulder is being pinched (e.g., your shoulder bursa, rotator cuff, biceps tendon). Further examination of your shoulder mobility and strength is needed to form a complete picture of your shoulder condition, and only a trained medical .Rotator cuff arthropathy is a pattern of joint degeneration due to loss of stabilizing function by the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff provides a net inferiorly directed force, balaced by a superiorly directed force by the deltoid muscle. In rotator cuff arthropathy the following findings can be seen: Massive rotator cuff tear
Rotator cuff tears, glenohumeral joint instabilities, and labral tears are associated with an increased incidence of subacromial impingement (1). The "cluster" of tests validated to rule in/rule out subacromial impingement only indicates the presence or absence of impingement (1). . The best combination of tests to detect a full-thickness RTC .
Rotator cuff tear is one of the most common shoulder diseases. It is interesting that some rotator cuff tears are symptomatic, whereas others are asymptomatic. Pain is the most common symptom of patients with a tear. . The lift-off test to detect a subscapularis tear was introduced by Gerber and Krushell .
A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11).
The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome.Rotator cuff injuries are common because you use them so often for so many activities throughout your day. Injuries can happen suddenly or build up over time. Rotator cuff damage is a common sports injury. The most common rotator cuff injuries include: Overuse syndrome. Shoulder impingement syndrome (rotator cuff tendinitis). Rotator cuff tears.
shoulder rotator cuff physical exam
self acl tear test
Looking for the latest PC video games? Look no further than t.
what test for rotator cuff tear|complete rotator cuff tear test